Sepsis is a medical emergency
Sepsis arises when the body’s response to an infection damages its own tissues and organs. It can lead to shock, multiple organ failures and death, especially if it is not recognized early and treated promptly. For patients with an infection, sepsis is the most common pathway to death. Worldwide around 9 million people die from sepsis every year.
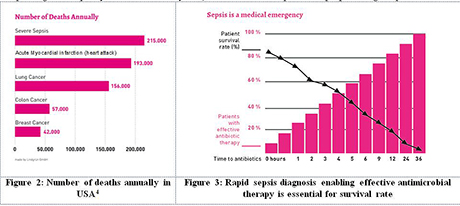
Number of deaths annually in the US/Rapid sepsis diagnosis is essential for survival rate
Source: http://www.dsxtherapeutics.com or www.sepsis.com
SmartDiagnos goes beyond state-of-the-art on these 5 diagnostic performance indicators:
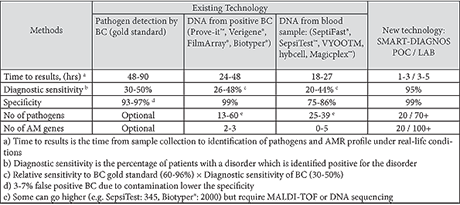
The technology
The proposed equipment is based on DNA-based KET (micro-nano-bio) for high-sensitive specific diagnostics. It will allow fast and precise sepsis diagnoses to initiate effective antimicrobial therapy. It will be developed in 2 versions for 2 types of applications:
- The POC system enables an evidence-based initial diagnosis to start sepsis treatment
- The LAB system enables an in-depth analysis providing the “bigger picture” and confirming or adjusting the initial diagnosis.
After the end of the project, a clinical performance test must be carried out prior to marketing.

Why are current solutions not good enough?
Existing commercially available solutions all suffer from either low diagnostic sensitivity, limited panel of pathogens, no or very limited test for antimicrobial resistance and complex handling and lengthy procedures.
![]() Graphic illustration of current procedure for sepsis diagnostic and treatment (click for larger illustration)
Graphic illustration of current procedure for sepsis diagnostic and treatment (click for larger illustration)
Source: Bloos, F., Sachse, S., Kortgen, A., Pletz, M. W., Lehmann, M., Straube, E., … Bauer, M. (2012). Evaluation of a polymerase chain reaction assay for pathogen detection in septic patients under routine condition: an observational study. PloS One, 7(9), e46003. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046003